GMAT Practice Test Guide - GMAT Practice Tests, Mock Tests, & Sample Tests.
In this guide you will learn about GMAT test questions and GMAT general exam information to help you prepare successfully for your GMAT test. This page contains everything you need to know and the essential skills for a high GMAT score.
Below you'll find our complete list of GMAT simulated online tests based on the new GMAT Focus Test. These GMAT simulated online tests will be available in January, 2024. Once they are available, click on any button to be taken to the test dashboard page. There you can select a full GMAT practice test to begin your training.
GMAT Practice Test Guide
The remainder of this guide will give detailed information about the GMAT test. You'll also find sample GMAT test questions for all sections.
Table Of Contents
The Introduction to the GMAT Focus Test
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is a standardized test widely used as an admissions requirement for graduate business programs, particularly for MBA (Master of Business Administration) programs. It is administered by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC).
The GMAT test is designed to assess various skills important for success in business and management studies. It contains three sections: Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA), Integrated Reasoning (DI), Quantitative Reasoning (Quant), and Verbal Reasoning (VR). However, A new version of the GMAT, named GMAT Focus, is set to be launched in December 2023. The GMAT focus test will contain only three sections: Data Insights (DI), Quantitative Reasoning (Quant), and Verbal Reasoning (VR).
The individual sections of the GMAT Focus test and their respective time allocations are as follows:
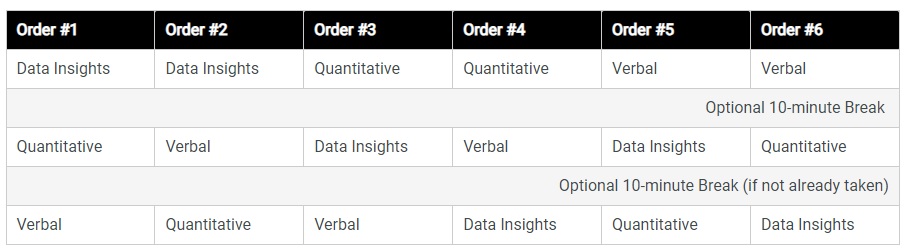
Also, before starting your test, you will be given the option to choose which order you will take your GMAT exam. You will see a table like the following:
Additional Features of the GMAT Focus Test
There are some new features of the new GMAT Focus test that the traditional GMAT test don’t have. These features give test-takers more flexibility while taking the exam. Pay attention to the follwing new features:
- You can now bookmark any questions you feel unsure about during the exam. Once these questions are bookmarked, you can go back to these questions to review and edit answers easily.
- You can review all answers at the end of each section, but you can only change your answers to three questions per section.
Computer Adaptive Format
Like the GMAT test, the new GMAT Focus test is also computer adaptive, which means the GMAT exam adapts questions continuously and automatically based on your individual ability level. Let’s see how it works:
2. As you answer each question, the computer assesses your response and utilizes it, along with your previous answers, to determine the subsequent question.
3. If you answer a question correctly, the computer will typically present a slightly more challenging one. Conversely, if you answer a question incorrectly, the next one will be slightly easier.
4. This process continues until you complete the section, at which point the computer will have an accurate assessment of your ability in that particular subject.
Therefore, as you answer more questions correctly, the computer adaptive sections will progressively present more difficult questions. However, if you encounter a seemingly easier question, it does not necessarily indicate that you answered the previous question incorrectly. The test needs to cover a range of content, both in terms of question types and subject matter presented. Your score is determined by the difficulty and statistical characteristics of the questions you answer correctly, as well as the number of questions you get right.
How the GMAT Focus Test is Scored
After you take the GMAT test, each section (Data Insights, Verbal Reasoning, and Quantitative Reasoning) will be scored on a scale between 60 to 90, with 1-point increments. Your GMAT Total score is then determined by your three section scores. The GMAT has an algorithm that will covert the sum of all three section scores into a score ranging between 205 and 805, in 10-point increments. Keep in mind that the total score is not a simple sum of the Data Insights, Verbal, and Quantitative scores.
Therefore, upon completing the GMAT Focus Edition, you will receive four different scores:
- The score for Data Insights (score between 60 to 90)
- The score for Verbal Reasoning (score between 60 to 90)
- The score for Quantitative Reasoning (score between 60 to 90)
- The GMAT Total score (score between 205 to 805, with 10-point increments )
Now, we have looked at the GMAT test on a higher level. Let's get into each section in detail.
Data Insights (DI)
The Data Insights (DI) section has 20 questions, and you will encounter a combination of the following 5 question types throughout the section.
- Graphics Interpretation
- Two-Part Analysis
- Table Analysis
- Multi-Source Reasoning
- Data Sufficiency
To practice all Data Insights questions, check out GMAT Data Insights Guide.
Table Analysis
In this type of question, you are asked to analyze data presented in a table format. The question comes with a sortable table of information, kind of like a spreadsheet. Look at the following example question:
The following table represents the feature quality ratings of five different video game consoles. Each feature is rated from 0 to 5, with 5 being the best quality. A console (P) is said to be ratings-dominant over another console (Q) if P matches or exceeds the ratings of Q on every single feature but Q does not match or exceed all of the ratings of P.
| Console | Feature 1 | Feature 2 | Feature 3 | Feature 4 | Feature 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
X1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
|
X2 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
4 |
0 |
|
XS |
1 |
1 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
|
XL |
0 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
|
XZ |
0 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
For each of the following consoles, select Yes if the console is ratings-dominant over any of the other consoles in the table. Otherwise, select No.
radio_button_uncheckedYes |
radio_button_uncheckedNo |
Console X1 |
radio_button_uncheckedYes |
radio_button_uncheckedNo |
Console XS |
radio_button_uncheckedYes |
radio_button_uncheckedNo |
Console XZ |
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Console X1: Yes (it is ratings-dominant over consoles XL and XZ)
Console XS: No (it is not ratings-dominant over any other console)
Console XZ: No (it is not ratings-dominant over any other console)
Graphics Interpretation
In this type of question, you are asked to analyze a graph, chart, or table to answer questions. Look at the following question from GMAT Offical IR Practice.
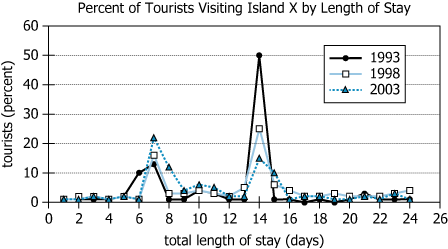
The graph indicates, for each of the years 1993, 1998, and 2003, the percent of the total number of tourists visiting Island X during each of those years by the length of those tourists' stays on the island.
Based on the assumption that the information provided is correct, select from each drop-down menu the option that completes the statement most accurately.
The combined probability that a tourist chosen at random had stayed either 7 or 14 days on the island was highest in and, to the nearest tenth, that probability was
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Answer: 1993 | 0.6
According to the graph, approximately 12% of the tourists in 1993 stayed on the island for 7 days, and 50% stayed for 14 days. Thus, 62% (12% + 50% = 62%) of the tourists in 1993 stayed on the island for either 7 or 14 days.
In 1998, 16% of tourists stayed 7 days and 25% stayed 14 days, for a combined total of 41% (16% + 25% = 41%) .
In 2003, 22% of tourists stayed 7 days and 15% stayed 14 days, for a combined total of 37% ( 22% + 15% = 37%).
Therefore, the percentage of tourists who stayed for either 7 or 14 days is greater in 1993 (62%) than in 1998 (41%) or 2003 (37%), making the probability that a randomly chosen tourist stayed 7 or 14 days greatest in that year.
The first correct answer is 1993.
The second correct answer is 0.6 as the combined probability that a randomly chosen tourist that year stayed 7 or 14 days is 0.62, which rounded to the nearest tenth is 0.6.
Two-Part Analysis
In this question type, you are asked to solve a problem by selecting two answers from multiple options. Look at the following example question:
Promotion: Our pioneering 20/18 reduced-interest loan is the ideal financial aid for swift business projects. Clients can receive a loan up to 85% of the value of their collateralized assets, with an upfront interest deduction of 20%, and are provided an 18-month period to repay the initial loan amount.*
*Loan Conditions: The actual loan proceeds, delivered by check in Euros, are calculated as the original loan sum minus the total loan interest — which is 20% of the original loan amount.
A 20/18 reduced-interest loan loan with amount n Euros is taken out by a business. Select the expressions for the repayment amount (the sum of the payments made to fully repay the loan) and the loan proceeds for this loan. Make only two selections, one in each column.
| Loan proceeds | Repayment amount | Expression (in Euros) |
radio_button_unchecked |
radio_button_unchecked |
0.15n |
radio_button_unchecked |
radio_button_unchecked |
0.80n |
radio_button_unchecked |
radio_button_unchecked |
0.2n |
radio_button_unchecked |
radio_button_unchecked |
1n |
radio_button_unchecked |
radio_button_unchecked |
1.2n |
radio_button_unchecked |
radio_button_unchecked |
1.15n |
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Answer:
Loan proceeds: 0.8n
Repayment amount: 1.00n
In this question, the business borrows an amount up to 85% of their collateral assets value, but that loan amount is given to them after deducting the 20% interest upfront. This means, for a loan of amount 'n', the actual loan proceeds (amount received by the business) would be 'n - 0.2n' which equals '0.8n'.
And, when it comes to repayment, the business needs to pay back the original loan amount, which is 'n', regardless of the deducted interest.
Multi-Source Reasoning
In this question type, you are asked to evaluate information from multiple sources to answer questions. Each question is accompanied by two or three sources of information displayed on tabbed pages, which can consist of a combination of text, charts, and tables.
Data Sufficiency
In this question type, you are asked to determine whether the given data is sufficient to solve a math problem. The math problem includes a question, accompanied by initial data, along with two statements labeled (1) and (2) that provide additional data. Your task is to determine if you have sufficient information to answer the question using either statement (1) or (2) alone, both of them together, or even with all the given data combined.
A basket contains blue, purple, and orange marbles. If you select a random marble from the basket, what is the probability that the marble will be either blue or orange?
(1) The probability to pick a blue marble is 1/3.
(2) The probability to pick a purple marble is 1/7.
-
radio_button_uncheckedStatement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient.
-
radio_button_uncheckedStatement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient.
-
radio_button_uncheckedBOTH statements TOGETHER are sufficient, but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient.
-
radio_button_uncheckedEACH statement ALONE is sufficient.
-
radio_button_uncheckedStatements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient.
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Answer:(B)
Statement (1):
This statement gives the probability of picking a blue marble, but leaves us with no information on the probability of picking an orange marble. This is insufficient.
Statement (1) ALONE is NOT sufficient.
Statement (2):
This statement provides the probability of picking a purple marble. Knowing that the only marbles in the basket are blue, purple, and orange, we can infer that the sum of the probabilities to pick a marble of each color is 1. Hence, P(purple) + P(blue) + P(orange) = 1. We can then subtract P(purple) from 1 to find P(blue) + P(orange). This is sufficient.
Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. Hence, B.
Quantitative Reasoning (Quant)
You will encounter 21 Problem Solving questions in the Quantitative Reasoning section. The Problem Solving questions require you to solve mathematical problems and select the correct answer from multiple-choice options. The GMAT Quantitative Reasoning questions test the following math concepts:
To practice all Quantitative Reasoning questions, check out GMAT Quantitative Reasoning Guide.
Let’s look at a few example questions.
X and Y are each 3-digit integers. Each of the numbers 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9 is a digit of either X or Y. What is the smallest possible positive difference between X and Y?
-
radio_button_unchecked(A) 19
-
radio_button_unchecked(B) 39
-
radio_button_unchecked(C) 47
-
radio_button_unchecked(D) 26
-
radio_button_unchecked(E) 17
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Answer: (D)
Since
- each of the 6 digits that are given must appear in X or Y
- both of X and Y are 3-digit numbers
We know that no digit can appear in both X and Y.
To find out the smallest possible difference X – Y, we first need to find the smallest possible difference of X - Y in the hundreds digits.
There are 3 cases in which the difference in the hundreds column has the minimal value of 1:
- 9 – 8
- 6 – 5
- 2 – 1
In each case, when the remaining digits are used as the tens and units digits of X and Y, the value of X should be least and the value of Y should be greatest.
Case 1: If the hundreds digits of X and Y are 9 and 8, respectively, then
X – Y = 912 – 865 = 47.Case 2: If the hundreds digits of X and Y are 6 and 5, respectively, then
X – Y = 612 – 586 = 26.Case 3: If the hundreds digits of X and Y are 2 and 1, respectively, then
X – Y = 256 – 198 = 58.Thus, the smallest positive difference between X and Y is 26.
The correct answer is (D).
A concert hall with 800 seats sells tickets at $2.00, $3.00, or $4.00 per seat. On Friday evening, 1/4 of the tickets sold were at $3.00 per seat and the total receipts from the sale of 800 tickets was $2,600. How many of the tickets sold were at $4.00 per seat?
-
radio_button_unchecked(A) 100
-
radio_button_unchecked(B) 200
-
radio_button_unchecked(C) 300
-
radio_button_unchecked(D) 400
-
radio_button_unchecked(E) 500
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Answer: (D)
Let's denote:
- x as the number of tickets sold at $2.00
- y as the number of tickets sold at $3.00
- z as the number of tickets sold at $4.00
From the problem, we can form the following equations:
- x + y + z= 800 (Total number of tickets)
- y=1/4 ∗ 800 = 200 (1/4 of the tickets were sold at $3.00)
- 2.00x + 3.00y + 4.00z = 2600 (Total sale was $2,600)
We can substitute y from equation 2 into equation 1
x + 200 + z = 800
x + z = 600W can substitute y from equation 2 into equation 3:
2.00x + 3.00∗200 + 4.00z = 2600
2.00x + 600 + 4.00z = 2600
2.00x + 4.00z = 2000
x + 2z = 1000So we get the following two equations
- x + z = 600
- x + 2z = 1000
Let's multiply the first equation by 2.00:
- 2x + 2z = 1200
- x + 2z = 1000
Now subtract this first equation from the second equation:
\( \frac { \begin{aligned} 2x+2z &= 1200\\ x+2z &= 1000 \end{aligned} } {x = 200} \ - \)
Finally, solve for z by putting x = 200 into the equation “x + z = 600”
200 + z = 600
z=400
So, 400 tickets were sold at $4.00 per seat. Hence, the correct answer is (D) 400.
Verbal Reasoning (VR)
The VR section assesses your ability to understand written material and evaluate arguments. It has 23 multiple-choice questions and includes two types of questions: Reading Comprehension and Critical Reasoning
Critical Reasoning
Critical Reasoning questions generally consist of
- A short reading passage that is often under 100 words. The passage presents an argument.
- A question that asks you which of the five answer options strengthens or weakens an argument, tells why the argument is flawed, or strongly supports or damages an argument.
To learn more about the 10 common question types of Critical Reasoning questions, check out GMAT Verbal Reasoning Guide.
Ylivar has developed an advanced electric vehicle that boasts a 40 percent longer range than the electric vehicle produced by its main competitor, Xellis, currently dominating the market in German. Ylivar's electric vehicle is particularly suitable for the growing demand among German's urban commuters, despite having a higher price tag compared to Xellis. The government of German has proposed implementing stricter emission standards within the next three years, requiring electric vehicles to surpass the current emissions threshold by at least 50 percent. Unfortunately, Xellis may struggle to upgrade its electric vehicle to meet these new standards. Therefore, if the proposed regulations are enacted, Ylivar's electric vehicle is expected to experience robust sales in German thereafter.
-
radio_button_uncheckedThe government of German will successfully implement the proposed stricter emission standards within the next three years.
-
radio_button_uncheckedYlivar's electric vehicle is the only electric vehicle in Elterra that can meet the proposed emission standards.
-
radio_button_uncheckedThe demand for electric vehicles among German's urban commuters will continue to grow in the coming years.
-
radio_button_uncheckedXellis will not be able to modify its electric vehicle to meet the new emission standards set by the government of Elterra.
-
radio_button_uncheckedThe higher price of Ylivar's electric vehicle compared to Xellis will not deter customers in Elterra from choosing the longer-range and more environmentally friendly option.
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation:
Answer: (B)
In the given argument, it is stated that Ylivar's electric vehicle has a 40 percent longer range than Xellis' electric vehicle and is particularly suitable for the growing demand among German's urban commuters. Additionally, the government of German has proposed implementing stricter emission standards, which requires electric vehicles to surpass the current emissions threshold by at least 50 percent. Due to this, Xellis may struggle to upgrade its electric vehicle to meet the new standards.
To support the conclusion that Ylivar's electric vehicle is expected to experience robust sales in Germany, there must be an assumption made. The assumption is the missing link that ensures the conclusion follows logically from the premises.
Let's evaluate the other answer choices and see why they are not correct:
(A) The government of German will successfully implement the proposed stricter emission standards within the next three years. This answer choice assumes the successful implementation of the proposed standards, but it does not directly relate to Ylivar's electric vehicle being the best option in the market to meet those standards. It is an assumption, but it doesn't address the core of the argument.
(B) Ylivar's electric vehicle is the only electric vehicle in Elterra that can meet the proposed emission standards. (Correct).The answer is (B) because it assumes that Ylivar's electric vehicle is the only electric vehicle in Germany that can meet the proposed emission standards. This assumption is important for the argument's conclusion to make sense. If there are other electric vehicles available in Germany that can also meet the emission standards, then Ylivar's vehicle may face competition and its expected robust sales may not be guaranteed. However, by assuming that Ylivar's electric vehicle is the only one that meets the emission standards, it strengthens the argument's claim that Ylivar will have a competitive advantage and will likely have strong sales in Germany.
(C) The demand for electric vehicles among German's urban commuters will continue to grow in the coming years. This answer choice talks about the demand for electric vehicles, but it does not directly impact whether Ylivar's electric vehicle will experience robust sales due to the new standards. It is not a critical assumption for the argument.
(D) Xellis will not be able to modify its electric vehicle to meet the new emission standards set by the government of Elterra. This answer choice comes close to being a relevant assumption, but it focuses on Xellis' ability to modify its vehicle rather than whether Ylivar's electric vehicle can meet the standards. The argument's main concern is whether Ylivar's electric vehicle is the only one capable of meeting the new emission standards.
(E) The higher price of Ylivar's electric vehicle compared to Xellis will not deter customers in Elterra from choosing the longer-range and more environmentally friendly option. While the price difference may be a concern, the argument is specifically centered around Ylivar's electric vehicle being able to meet the proposed emission standards. The assumption needs to address the vehicle's capability to meet those standards, not customer preferences based on price and features.
Reading Comprehension
Each Reading Comprehension passage is accompanied by several questions that require you to identify the main idea, understand the supporting ideas, draw the inference, find out relationships between ideas, or evaluate the organization/logic from the reading passage.
The reading passage typically spans around 350 words and covers topics from various domains, such as:
- Social sciences or humanities
- Physical or biological sciences
- Business-related fields like marketing, economics, and human resource management
For further information on the five specific types of Reading Comprehension questions, check out GMAT Verbal Reasoning Guide.
Let's look at the following sample question:
Emiko Tanaka's research regarding the early Chinese immigrants to Oregon's Willamette Valley sheds light on the evolution of fishing communities from 1880 to 1930. The first-generation immigrants (Yisei) were brought to the Willamette Valley primarily to fish for salmon. Just as Yisei workers in urban areas, Chinese men in rural settings procured work through the “contractor” system. This model had three primary components: immigrant wage earners; Yisei hostels where workers resided; and job brokers, responsible for assembling workers for specific tasks and then brokering an agreement between workers and their employers. This system was initially used by Filipino laborers who had come before the Chinese. A parallel institution was the “employment guild”, which offered employment details and brokered work contracts, and other legal dealings like land lease agreements for Yisei who opted in and provided an annual membership fee to the cooperative.
When the salmon stocks began to deplete in 1908, the Yisei started to lease land from the valley's apple orchard owners. The Chinese offered labor, and the yield was shared between the laborers and the landowners. The Yisei thus transitioned swiftly from wage labor to a profit-sharing model. A modicum of economic advancement was seen as some Yisei had the means to directly lease or purchase orchards, while others collaborated to establish orchard consortiums. As the Yisei began managing orchards, they started to establish families, giving rise to a settled Chinese American community. Regrettably, the Yisei's ambitions to attain agricultural self-sufficiency were thwarted by restrictive government legislations, like the Foreign Soil Act of 1910. However, immigrants found loopholes in these laws by leasing or acquiring land in the names of their children born in America.
Tanaka's detailed analysis of one rural Chinese American community offers insightful data about the Yisei’s lives and experiences. Nonetheless, it's quite specific in its scope. This specificity arises from Tanaka’s method of employing oral narratives, which can't replace a more expansive theoretical or comparative standpoint. Subsequent studies could explore two pertinent topics hinted by her research: were the Yisei of the Willamette Valley analogous to Yisei in cityscapes, and what discrepancies were evident between rural Chinese American communities?
Which of the following best describes an “employment guild,” as defined in the passage?
-
radio_button_uncheckedAn obligation for every Yisei if they wished to find work in Willamette Valley.
-
radio_button_uncheckedA union with members comprising job brokers and influential landowners.
-
radio_button_uncheckedAn orchard consortium initiated by long-residing Yisei in the Willamette Valley.
-
radio_button_uncheckedA membership-based association for Yisei workers who paid fees.
-
radio_button_uncheckedA communal organization for Chinese laborers and their kin.
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation
Answer: (D) A membership-based association for Yisei workers who paid fees.
The passage defines the “employment guild” as a parallel institution to the “contractor” system, offering employment details, brokering work contracts, and handling other legal matters. Yisei who opted to be a part of it provided an annual membership fee. This directly aligns with the option that describes it as a membership-based association for those who paid fees. The other options either add information not present in the passage or inaccurately reflect the guild's purpose and membership.
Several Yisei families collaborate to lease an apple orchard and the required farming tools. This scenario best mirrors which of the described situations in the passage?
-
radio_button_uncheckedA standard profit-sharing model.
-
radio_button_uncheckedAn orchard consortium.
-
radio_button_uncheckedAn “employment guild.”
-
radio_button_uncheckedThe “contractor” system.
-
radio_button_uncheckedBypassing the Foreign Soil Act.
-
spellcheck Check Answer & Answer Explanation
Answer Explanation
Answer: (B) An orchard consortium.
The passage states that some Yisei collaborated to establish orchard consortiums as a method of economic advancement. This suggests that they were collectively managing or leasing orchards. The described scenario in the question where several Yisei families come together to lease an apple orchard matches this description. The other options, such as the “employment guild” or the “contractor” system, don't specifically deal with multiple families managing land or orchards, making the correct answer "an orchard consortium."